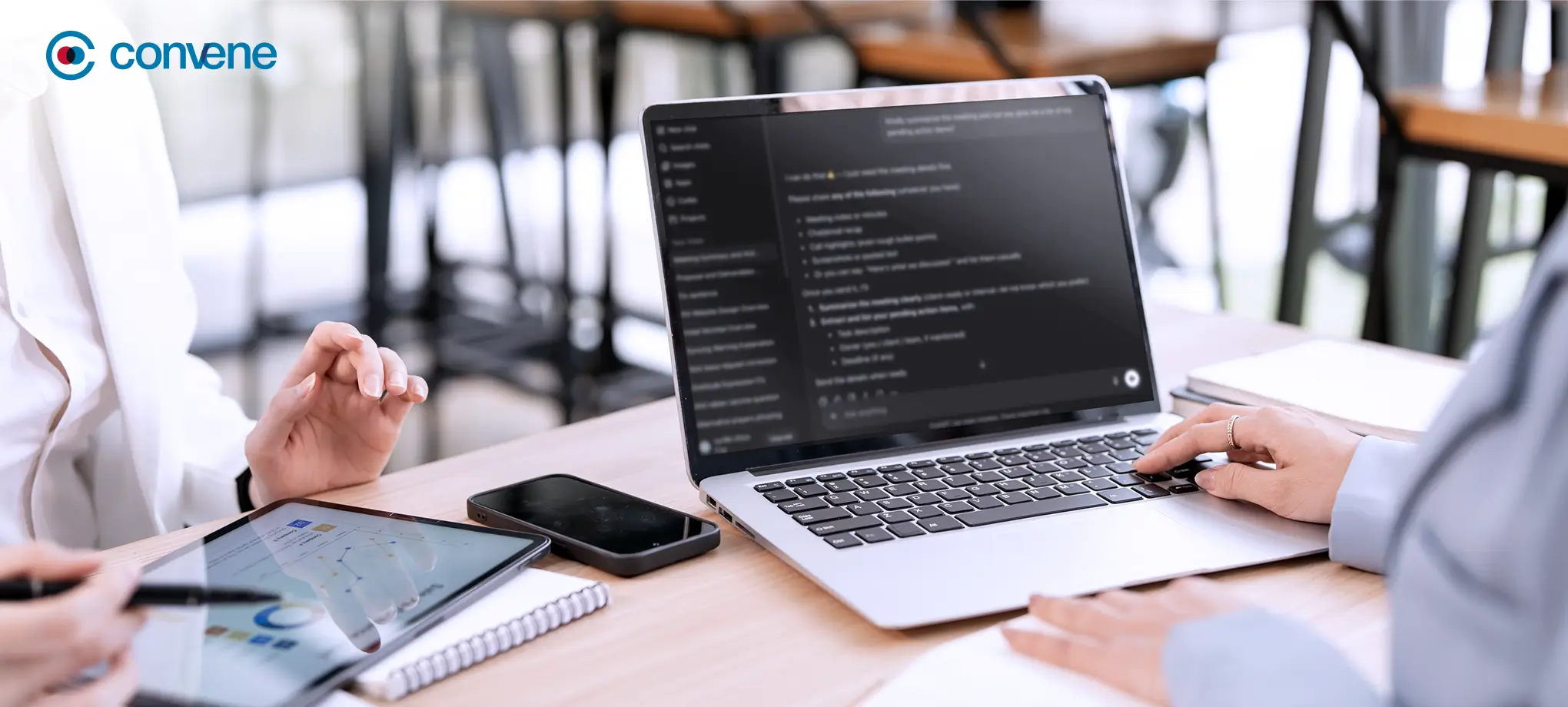
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a thing of the future or a tool used only by large tech companies. Look around today’s workplace, and you’ll see it helping people draft emails, analyze data, even schedule meetings — it’s everywhere.
According to a recent study by the National Bureau of Economic Research, AI adoption in the workplace has grown quickly since its mainstream use in 2022. The study reports that 28% of employed participants have used generative AI tools such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini at work, and 10.6% use them daily.
As AI tools become more common, organizations have to figure out quickly how to use them effectively.
How AI Has Changed the Workplace in Recent Years
Not long ago, most workplaces depended on manual processes and clearly defined roles. Information moved slowly through meetings, memos, and long email threads. Decisions were often based on past data and personal judgment, while technology was treated as a “nice-to-have” rather than a key part of the decision-making process.
The modern workplace looks very different. Work is mostly digital, fast-moving, and often distributed across teams and time zones. Decisions must be made quickly, and collaboration is constant. To keep pace, organizations have made technology a central part of how work gets done, ensuring a comprehensive IT stack to support quick and informed decisions.
AI speeds up this shift even further by adding automation and machine learning to everyday tasks. This lets teams focus on more important work. In fact, a recent study by McKinsey shows that nearly 90% of companies now use AI regularly in at least one business function, with many reporting measurable productivity gains.
Common Use Cases for AI Across the Organization
How is AI used in the workplace? How does it assist different business functions? Listed below are some common examples of AI in the workplace:
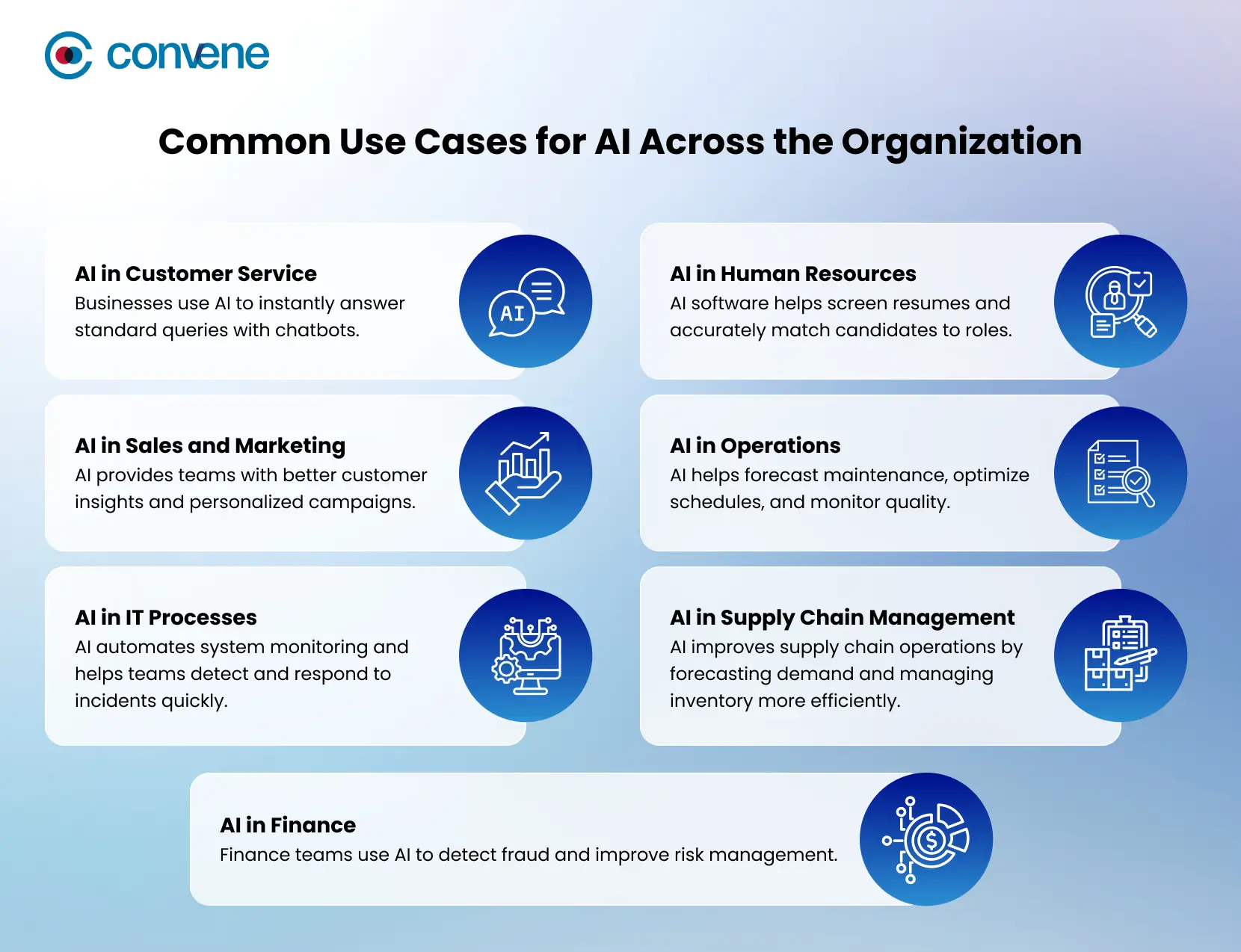
AI in Customer Service
Customer service teams use AI to instantly answer standard queries with chatbots and virtual assistants, which are often available at any time of day. Companies that offer ride-sharing and delivery services like Lyft and Domino’s use conversational AI to help customers with bookings, order tracking, and FAQs, making service faster and more accurate. Additionally, AI helps analyze customer feedback and history, providing human agents with better context once the inquiry reaches them, leading to higher-quality resolutions and greater satisfaction.
AI in Human Resources
HR teams use AI to make each step of recruitment, from onboarding to employee development, more efficient. AI software for HR is specialized to help screen resumes, find skill gaps, and match candidates to roles more accurately. Personalized onboarding helps new hires get up to speed quickly. AI also analyzes employee surveys and feedback to spot trends, like stress or burnout, so managers can step in early and offer support.
AI in Sales and Marketing
AI provides sales and marketing teams with better customer insights, lead scoring, and personalized campaigns. E-commerce companies like Amazon use machine learning to recommend products and send targeted messages based on customer behavior, increasing engagement and sales. Marketing teams can also test different content and adjust budgets in real time, improving results and reaching the right audience.
AI in Operations
Operations teams use AI to automate routine work and manage resources more effectively. In many industries, AI helps forecast maintenance, optimize schedules, and monitor quality. Manufacturers are using AI inspection systems to catch defects early, while logistics teams use route optimization to deliver faster and cut lead times. These improvements lower costs and make daily operations more reliable.
AI in IT Processes
In IT, AI automates system monitoring, detects problems early, and helps teams respond to incidents before they become bigger issues. For example, tools like those from Moveworks use natural language understanding to handle IT service requests and resolve help desk tickets automatically, cutting down resolution times for companies such as Autodesk and Broadcom. AI also improves cybersecurity by scanning network activity for suspicious behavior, making defenses stronger without needing constant manual checks.
AI in Supply Chain Management
AI improves supply chain operations by first and foremost forecasting demand, as well as managing inventory and spotting possible disruptions. Advanced algorithms look at past data, market trends, and other external factors like weather or global events to predict risks and adjust buying strategies. Many companies across the globe now use AI to handle supply chain challenges, making sure products are available when and where needed.
AI in Finance
Finance teams use AI to improve risk management, detect fraud, and speed up planning. Large financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase use AI tools such as COiN to automate legal and compliance reviews, saving thousands of staff hours and increasing accuracy. AI also helps with cash flow forecasting and scenario analysis, giving finance leaders faster, data-driven insights for budgeting and strategy.
Benefits of Using AI in the Workplace
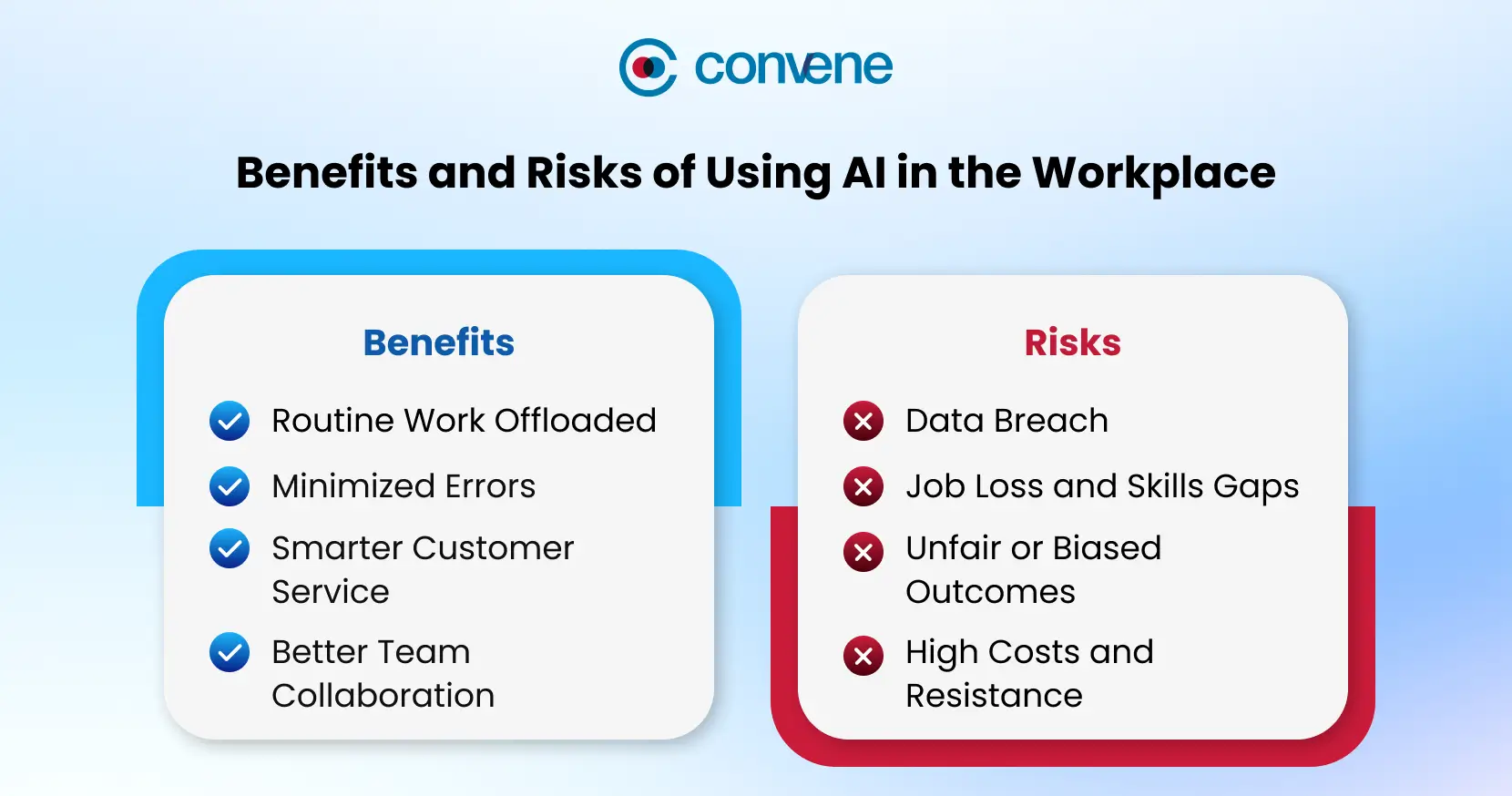
The most successful organizations treat AI as a partner. How does that work? Humans provide judgment, creativity, and emotional intelligence, while AI contributes speed, scalability, and pattern recognition. This partnership brings several key benefits, such as:
Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Day by day, AI is becoming a normal part of how teams work and collaborate because it delivers real, measurable results. In global surveys, 94% of employees in organizations using generative AI said it improved team performance, and almost all felt confident in their problem-solving skills with the help of AI.
AI boosts productivity by automating routine, time-consuming tasks like report generation and scheduling. By doing so, it lets employees focus on work that needs critical thinking. Teams can also finish projects faster. For example, AI-powered project management tools help track progress, spot bottlenecks, and improve workflows, so teams get more done in less time without losing quality.
Reduced Human Error
Human errors, especially in data-heavy or repetitive tasks, can be costly and may even harm a company’s reputation. AI helps reduce these mistakes by automating calculations, processing large datasets, and flagging unusual patterns that might be missed. This leads to higher accuracy, better decisions, and lower operational risk.
Improved Customer Experience
AI improves customer interactions by making service faster and more personalized. Organizations can set up chatbots to answer common questions right away, while recommendation engines suggest products or services that fit each customer. AI-powered sentiment analysis also helps businesses spot issues early and adjust their offerings, leading to better experiences and stronger customer loyalty.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
AI makes collaboration easier by keeping teams aligned and informed. Meeting assistants can automatically summarize discussions and track action items, while real-time translation and document sharing help global teams work together smoothly. AI can also deliver the right information to the right people by using intelligent routing and predictive analysis, saving time and improving coordination.
Risks and Implications of Using AI in the Workplace
While the benefits of AI in the workplace are significant, it does not come without risks. McKinsey’s 2025 report on using AI at work reveals growing employee concerns about gen AI, with cybersecurity (51%) and inaccuracy (50%) topping the list. This is followed by personal privacy (43%), intellectual property infringement (40%), and workplace displacement (35%).
These concerns are not just about technology. They can affect trust, morale, and how willing employees are to adopt AI. When people feel unsure about how AI will impact their roles or data security, resistance is likely. That is why organisations need to address both the capabilities of AI and its impact on people and processes.
Data Privacy and Security
In January 2026, the interim chief of the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) uploaded sensitive government documents to a public version of ChatGPT. Although the documents were “unclassified but for official use only,” the incident triggered internal security reviews and highlighted the risks of employees using AI tools without proper controls.
AI systems handle large volumes of data, so security and privacy are critical, especially in high-risk domains, such as healthcare and government. Organizations need robust security measures like multi-level encryption, access controls, and regular audits to protect sensitive information. Clear data policies and adherence to regulations such as GDPR and U.S. federal laws help keep employee and customer data secure. Taking these steps early reduces legal risks and builds trust in AI adoption.
Job Displacement and Skills Gaps
Job displacement is a common concern in the first steps of AI adoption. However, it is important to note that while some routine tasks may go away, new roles and opportunities will also appear.
Organizations can help by following a three-step reskilling roadmap:
- First, by identifying at-risk roles that are most likely to be affected by AI integration.
- Next, mapping out new competencies required for emerging roles, thus providing a clear understanding of the skills employees need to thrive.
- Lastly, launching micro-learning sprints and workshops to quickly equip employees with the necessary skills.
Organizations should communicate clearly about how AI will affect work and help employees build the skills they need. This keeps the workforce adaptable and reduces anxiety.
Ethical and Bias Considerations
AI can create ethical challenges, such as bias and unintended results from automation. A most recent example of this occurred when Google’s Nano Banana Pro generated stereotypical ‘white saviour’ images in response to humanitarian prompts, despite no such racial framing being provided in the input. This would be avoided by regularly reviewing AI processes and results to ensure fairness and align with company values. It is also important to assign clear responsibility for ethical oversight. Appointing a dedicated role, such as a Chief Ethics Officer, for bias reviews and ethical decisions, or setting up oversight committees, helps organizations make responsible choices.
Integration and Implementation Challenges
Bringing AI into current workflows and systems can be challenging. Organizations need to consider compatibility, cost, and possible disruptions. However, it is also crucial to acknowledge the often-overlooked costs of cultural change. These can include the need for adjustments in team dynamics, resistance from employees, and shifts in workplace culture that require investment in communication and change management strategies.
Success depends on teamwork between technical staff and department leaders, careful planning, and, at times, adapting workflows to fit AI tools. Clear communication and good planning, addressing both technical and cultural aspects, help make the transition smooth and maximize the benefits of AI.
Best Practices for Deploying Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace
The success of AI depends more on leadership than on technology alone. When you are deploying or at the stage of considering the use of AI in the workplace, here are some steps that the board and executives must keep in mind:
1. Start with clear business goals
The same McKinsey study cited earlier reports that 92% of executives plan to increase AI spending in the next three years, but higher investment means higher expectations for results. Begin by identifying where AI can add measurable value, set clear success metrics, and review your priorities regularly as technology and business needs change. This is one sure way to ensure you reap the benefits of artificial intelligence in the workplace.
2. Choose the right AI tools
Not every organization needs the same AI capabilities. That is why leaders should first assess where AI will be used, whether for workflow automation, data analytics, or content creation, before choosing tools. Here are some commonly used AI tools for different workplace needs:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI): The most widely used AI tool in recent years, this generative AI assistant is best suited for drafting documents, summarizing information, answering questions, and brainstorming ideas.
- Microsoft 365 Copilot: AI embedded in Word, Excel, Outlook, and Teams to generate content, analyze data, and streamline workflows. This is ideal for teams that are already using Microsoft 365.
- Workday AI: Uses AI to support HR functions such as workforce planning, talent management, performance insights, and skills analysis.
- Asana AI: Supports project management by automating task updates, prioritization, and workflow rules, so teams and other stakeholders can stay on track.
- Power BI (with AI features): Applies AI to business intelligence and reporting, enabling teams to surface insights, spot trends, and make data-driven decisions.
3. Invest in people, not just tools
Beyond the tools, you should also take extra care of the people who use them. Adoption improves when employees know how AI works, how it supports their work, and where their judgment is still needed. Formal training is the most effective way to drive AI adoption prior to full-scale integration. Pilot programs and incentives, such as recognition or rewards, may also help encourage employees to embrace new workflows.
4. Build trust through transparency
Users adopt AI more readily when they understand what it does and how it uses data. As such, it is important to ensure that AI decisions are understandable and unbiased. Stanford’s Center for Research on Foundation Models (CRFM) created a Transparency Index to assess the transparency of foundation‑model developers on their model capabilities and governance practices. This highlights how much (or how little) information companies disclose about the models that increasingly shape our work and society, and can help your board and executives evaluate AI vendors and ensure responsible AI adoption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Artificial Intelligence at Work
What are the types of AI in the workplace?
Organizations use machine learning, such as deep learning, to analyze data and make predictions; natural language processing (NLP) to understand and generate text, powering chatbots and document tools; generative AI to create content like text, images, or code; and automation AI to handle repetitive tasks and streamline workflows.
What is the 30% rule in AI for companies?
The 70/30 rule, as others call it, suggests that organizations can automate up to 70% of routine, data-heavy work, freeing employees to focus on the remaining 30% of tasks that require complex problem-solving and human insight.
How to use AI safely in the workplace?
To use AI safely, organizations should protect sensitive data, comply with relevant regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA, regularly review AI outputs for errors or bias, and educate employees on responsible AI use and the limits of automated decision-making.
Lead with Confidence in an AI-Driven Workplace with Convene Board Portal

Leading with confidence in an AI-driven workplace is not just about technology. It is about making work easier and smarter for your people. Convene board portal helps by keeping communication secure, decisions clear, and governance organized on a single platform.
Now with Convene AI, board meetings get even smarter and more effective. Through this feature, you’ll get:
- Automated summaries of meetings, so you can catch up quickly
- Action suggestions and follow-up tasks
- Clean, clear meeting AI-generated minutes
- Smart and personalized assistance within the app, so it’s easier to navigate the platform
Convene AI is powered by AWS Bedrock to ensure a secure data environment and maintain enterprise-grade security, compliance, and data privacy for all your sensitive business information.
Make your board meetings more productive, transparent, and aligned with best governance practices. Want to see how it works? Book a demo today.
Jess is a Content Marketing Writer at Convene who commits herself to creating relevant, easy-to-digest, and SEO-friendly content. Before writing articles on governance and board management, she worked as a creative copywriter for a paint company, where she developed a keen eye for detail and a passion for making complex information accessible and enjoyable for readers. In her free time, she’s absorbed in the most random things. Her recent obsession is watching gardening videos for hours and dreaming of someday having her own kitchen garden.











