In ESG reporting, an increasing number of companies and public institutions are choosing to adopt the SASB standards. These standards assist them in improving sustainability performance and building trust among the public.
What is SASB?
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting has become a cornerstone for investors and stakeholders assessing a company’s long-term viability. By evaluating ESG factors, they gain critical insights into a company’s sustainability practices and potential risks.
Established in 2011, the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) is an independent, non-profit organisation based in San Francisco, California. SASB’s mission is to develop and disseminate sustainability accounting standards, enabling businesses to identify, manage, and communicate sustainability information to investors and other stakeholders.
SASB standards are particularly known for their industry-specific focus, providing clear and concise guidelines that help companies present relevant data consistently. This common language for sustainability reporting facilitates transparency and comparability across industries.
In 2021, SASB’s role became even more significant when it merged with the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) to form the Value Reporting Foundation (VRF). This merger paved the way for a stronger alignment with global reporting frameworks. In 2022, the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation announced the establishment of the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), which further consolidated global sustainability reporting standards.
Now, under the umbrella of the ISSB, SASB standards are being integrated with other frameworks to create a comprehensive, globally accepted set of sustainability disclosure standards. This integration ensures that companies not only adhere to SASB’s rigorous, industry-specific metrics but also align with the broader global sustainability standards set by the IFRS Foundation.
What is the ISSB?
The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) is an independent organisation established to develop global sustainability disclosure standards. Founded and operating under the IFRS Foundation, the main goal of ISSB is to create a unified system for sustainability reporting.
Its standards are designed for global applicability in mind, ensuring that sustainability information is relevant and comparable across countries and industries.
It is important to note that the ISSB sets global standards for sustainability reporting applicable across all sectors, aiming for a global approach. SASB, on the other hand, focuses on industry-specific standards, providing detailed guidance on what matters most to each sector.
What is the SASB Framework?
The SASB Framework is a comprehensive system designed to guide companies in disclosing sustainability information in a way that’s relevant and useful for investors.
It consists of more than 77 standards, each tailored to different industries, ensuring that the sustainability reporting is specific to the unique challenges and opportunities of each sector.
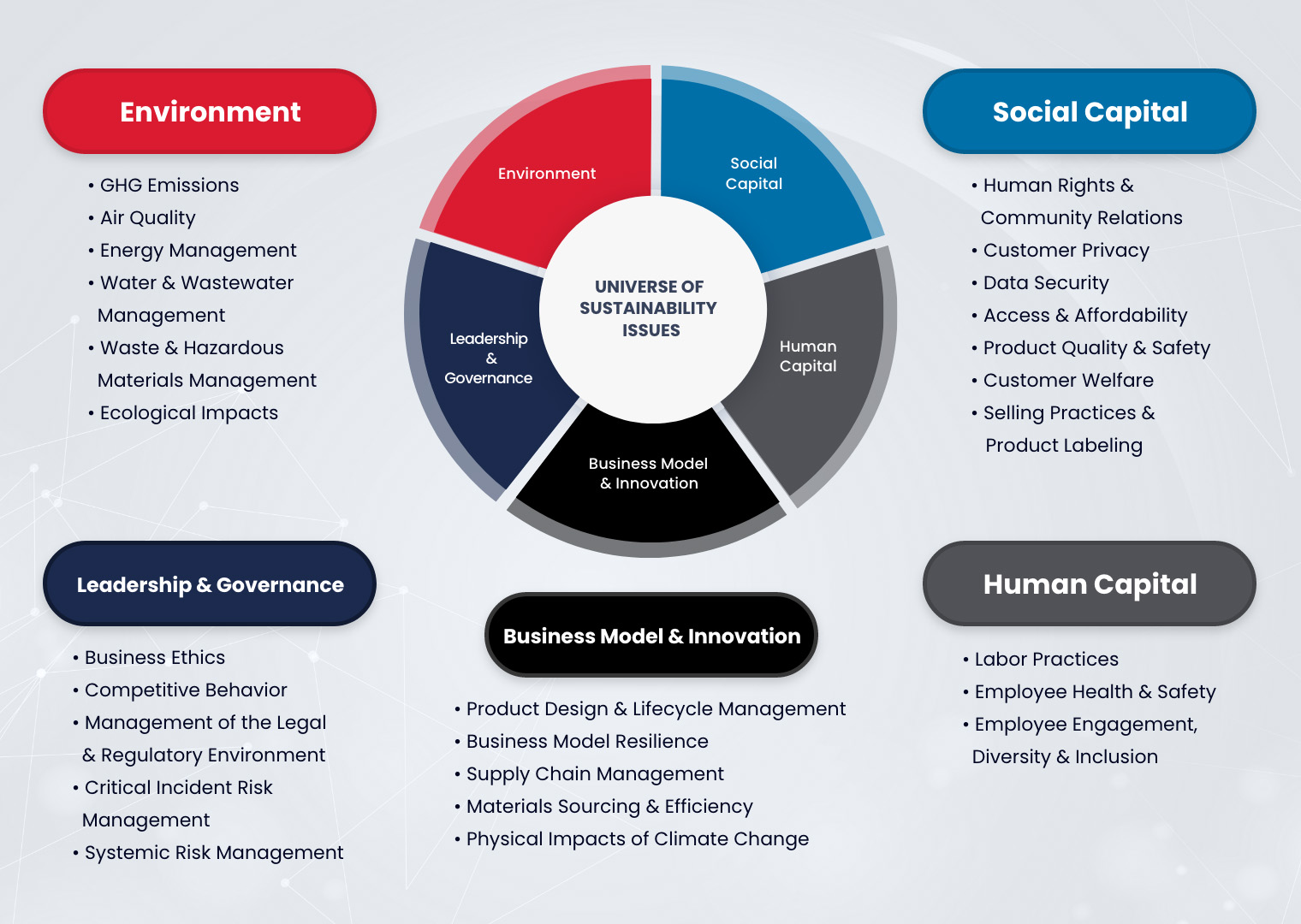
The framework is structured around five key issue categories:
- Environment – This includes topics like resource use, emissions, and environmental impact.
- Social Capital – Focuses on relationships with customers, suppliers, and the broader community, covering issues such as data privacy and product safety.
- Human Capital – Addresses labour practices, employee relations, and skills development.
- Business Model and Innovation – Covers how sustainability influences a company’s business model and its capacity for innovation.
- Leadership and Governance – Involves oversight, ethics, and management practices related to sustainability.
Each standard within the SASB Framework is designed to highlight the ESG issues that are financially material to specific industries.
For instance, the standards for the healthcare sector might emphasise patient safety and access to care, while those for the technology sector might focus on data security and intellectual property.
The SASB standards are organised into 26 detailed categories, such as labour relations, data security, and business ethics.
By focusing on these financially material issues, the framework helps companies report on aspects of their sustainability performance that are most relevant to investors and stakeholders, making the information both practical and impactful.
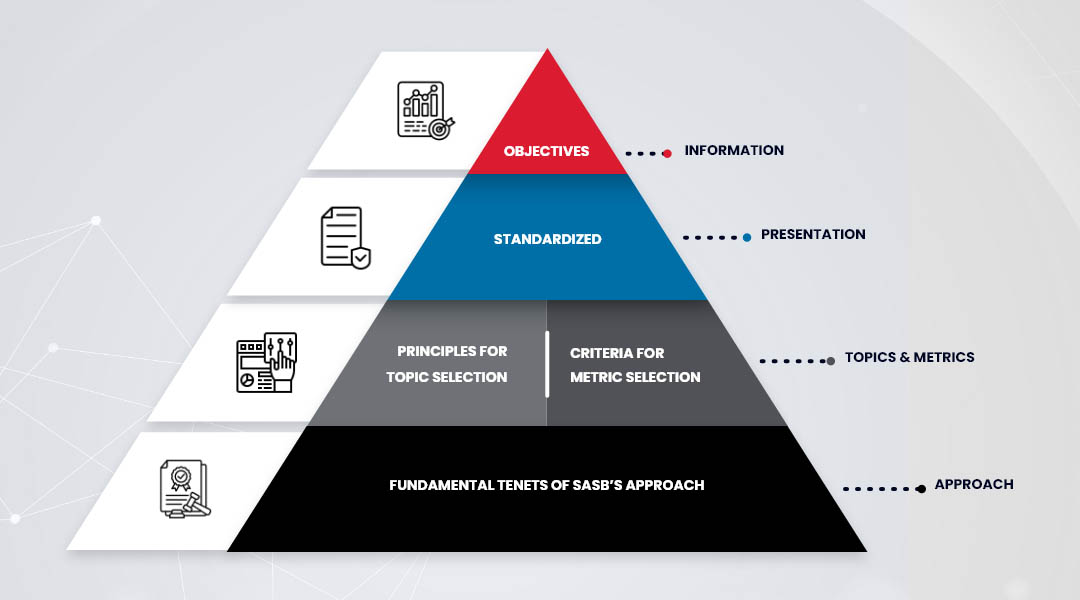
What are the SASB Standards and Principles?
Sustainability issues vary from industry to industry. Even organisations within the same sector may encounter problems unique to their operation.
Grounded in a standard-setting approach and based heavily on industry-specificity and financial materiality, SASB Standards and Principles provides a robust framework for clear, concise, and meaningful sustainability reporting.
These key principles include:
Global Applicability
One of the priorities of the SASB framework is to provide disclosures that are consistent and comparable in organisations across the globe. This means that all information in the report is understood within the same industry, regardless of the company’s country of origin and operation.
Financial Materiality
The SASB framework identified the most pressing ESG issues that impact 77 different industries. Their focus is on sustainability factors that impact a company’s financial performance.
Evidence-based
Through evidence gathered from external sources, the SASB framework is developed based on the proven financial impact of each sustainability issue.
Industry-specific
Recognising that not all sustainability concerns are equally relevant to every sector, the SASB standard provides industry specific concerns.
Market-informed
The SASB solicits relevant and timely information from subject-matter experts, corporate professionals, and investors to keep their guidelines up-to-date with the current market conditions.
What is Financial Materiality?
Financial materiality is a concept that focuses on identifying which environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors could affect a company’s financial health and business operations.
It ensures that ESG program reports present information that is directly relevant to stakeholders, highlighting aspects that could materially impact a company’s financial performance and long-term viability.
As previously mentioned, ESG reports have become crucial in presenting a company’s viability and longevity.
Each item in the report must be relevant and useful to stakeholders. Financial materiality ensures that all parts of the disclosure work together to provide a clear picture of the operation’s health, enabling investors and other stakeholders to make informed decisions.
In recent years, the concept of double materiality has become more popular as it expands the focus beyond financial impacts.
Double materiality acknowledges that not only should companies disclose ESG factors that affect their financial health (financial materiality), but they should also report on how their operations impact society and the environment (environmental and social materiality).
This broader perspective encourages businesses to consider and communicate their influence on a wider array of stakeholders, including communities, employees, and the planet.
SASB Materiality Map

The SASB Materiality Map is a user-friendly tool designed to identify which sustainability issues are most relevant in a specific industry. It serves as a guide that highlights key ESG factors for various sectors, making it easier to focus on what matters most.
The map breaks down sustainability issues by industry, so companies can quickly identify and address the factors that are critical to their sector.
The Materiality Finder, on the other hand, is a complementary online tool that offers a search function to locate SASB standards and industry-specific issues. This tool allows users can quickly search for relevant standards by entering their industry or specific topics, streamlining the process of accessing the most pertinent ESG guidelines.
Together, these help organisations focus their reporting efforts on the most critical sustainability issues for their sector, ensuring more targeted disclosures.
What is the Conceptual Framework Exposure Draft?
The SASB updates the Standards with the help of concerned members of the public through an exposure draft, a proposed updated text released for public comment.
The concepts and proposed changes are relayed to readers through a Conceptual Framework document. It details the basic concepts, principles, definitions, and objectives used by the Standards Board and technical experts to develop SASB disclosure standards. The Conceptual Framework is also used to inform external stakeholders — companies, regulators, investors, lenders, and creditors. It’s also imperative that service providers, such as accountants, auditors, and securities lawyers, are kept in the know.
The exposure draft also contains a description of the Rules of Procedure, detailing the policies and practices used by the Standards Board to develop, issue, and maintain the SASB
Standards.
The Rules of Procedure and the Conceptual Framework documents are intended to be used in conjunction and are freely accessible online. Used together, they keep stakeholders and other concerned parties informed of the SASB’s latest regulatory and framework developments.
Linking SASB Standards with Other Reporting Frameworks
Successful SASB reporting depends on integrating sustainable practices of an organisation as well as the education of employees on ESG-related matters. Some initiatives will enable you to gradually realign everyday practices with more sustainable standards. These include developing and implementing a comprehensive ESG strategy to lead the implementation of relevant practices to further the cause. As a result, you’ll find it easier to identify relevant areas in need of improvement and those to be reported on through the SASB framework.
Although the SASB Standards are intended for use by providers of capital, such as shareholders and creditors, they can be used with a wide array of additional ESG reporting frameworks and standards. For example, the SASB is tailored for use alongside standards from over 200 organisations, including EPA, OSHA, and IPIECA, as well as reporting frameworks such as:
TCFD
The Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) is charged with developing recommendations for improved and increased disclosures of climate-related financial risks. It empowers companies to assess future issues concerning financial materiality. The SASB, on the other hand, is more focused on past activities. The financial materiality information it identifies can be used to better understand and anticipate potential future issues.
GRI
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards exist to help reporting entities track, manage, develop, and publish sustainability metrics and data. The GRI Standards are intended for reporting on a wide range of sector-overarching ESG matters, including economic and ecological impacts on governments, investors, and labour organisations. SASB resources can be leveraged to enhance the financial materiality aspects of reports submitted through the GRI Standards.
CDP
Formerly known as the Carbon Disclosure Project, the CDP focuses on environmental and climate matters as they relate to the fiduciary duties of large, publicly traded companies. Combining the SASB with the CDP framework can be an effective way to cover a wider base of ESG-related matters, both ecological and financial, in disclosure reports.
Other factors to consider in SASB reporting include knowing which of the 77 standards to use and how to disclose your findings. Choosing the most appropriate industry standard will simplify identifying and assessing climate-related financial material matters. Companies can also choose to disclose through a variety of media, such as stand-alone SASB reports, annual shareholders’ reports, integrated reports, and investor relations websites, adhering to regulatory requirements.
Lastly, it’s important to establish effective channels of communication between governance, workforces, investors, and consumers in order to make regular improvements to your SASB reporting practices.
What are the benefits of SASB Certification?

SASB Certification is a recognised standard that companies can achieve by aligning their sustainability disclosures with the guidelines set forth by the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
Having this certification shows that a company has adopted industry-specific standards to report on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors that are financially material to their operations.
SASB Certification provides several key benefits for companies and investors alike, including:
Enhanced Transparency
SASB certification enables companies to disclose sustainability information clearly and relevantly, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and assess their practices.
Industry-Specific Guidance
The SASB framework provides guidelines tailored to the unique challenges and opportunities of each sector, so that reported information addresses the most pertinent issues for each industry.
Improved Comparability
Certification standardises sustainability data across companies within the same industry, which helps in making more informed decisions and allows for effective performance benchmarking.
Increased Credibility
Achieving SASB certification demonstrates a commitment to high-quality and standardised sustainability reporting, boosting the company’s reputation and reliability among stakeholders.
Better Risk Management
By focusing on financially material ESG factors, SASB certification helps identify and manage potential risks that could impact financial performance, leading to more effective risk mitigation strategies.
How to Apply SASB Standards for ESG Reporting
Applying SASB standards for ESG reporting involves several key steps to ensure that sustainability disclosures are relevant, accurate, and aligned with industry expectations:
1. Understand Industry-Specific Standards
The first step in adapting the SASB framework is by identifying the standards that apply to the industry. SASB provides tailored guidelines for 77 different sectors, so selecting the standards that address the most material ESG issues for the specific field is crucial.
2. Assess Financial Materiality
Companies need to focus on ESG factors that are financially material to their business. SASB standards emphasise reporting on issues likely to impact financial performance, helping prioritise and disclose the most critical information.
3. Gather and Analyse Data
Collecting data related to the identified ESG factors is essential. This includes both quantitative metrics and qualitative information about the company’s policies and practices. Ensuring that the data is accurate, comprehensive, and up-to-date is key.
4. Integrate with Financial Reporting
ESG disclosures should be aligned with traditional financial reports. SASB standards are designed to complement financial reporting, providing a holistic view of the company’s performance and helping investors understand how ESG issues impact financial outcomes.
5. Communicate Clearly and Consistently
The information should be presented clearly, concisely, and consistently. Using SASB’s guidance to structure reporting ensures that it meets the needs of investors and other stakeholders for comparability and relevance.
6. Review and Improve
Regular review and updates of ESG software for reporting are necessary to reflect changes in industry standards, company practices, and stakeholder expectations. Continuous improvement helps maintain the quality and relevance of sustainability disclosures.
Common SASB Questions, Answered:
Are the SASB Standards relevant on a global scale?
Yes, the SASB Standards are designed to be globally relevant. They provide a framework for sustainability reporting that helps companies across various industries to disclose ESG information consistently. The SASB Materiality Map is particularly useful for identifying which sustainability issues are most pertinent to different sectors, ensuring that the standards are applicable worldwide.
How can one begin ESG reporting using the SASB Standards?
To start ESG reporting using the SASB Standards, a company should first familiarise itself with the SASB Framework, which outlines the key standards for various industries. Utilising an ESG platform or ESG reporting software can simplify the process of integrating these standards into their sustainability reporting. Companies can also seek SASB Certification to validate their adherence to these standards and improve the credibility of their sustainability report.
What should a company do if it operates across multiple industries?
If a company operates across multiple industries, it should consult the SASB Materiality Map to identify the most relevant SASB Standards for each sector. This approach ensures that the company addresses the specific ESG issues pertinent to each industry in its sustainability reporting. Using sustainability software that supports multi-industry reporting can also help manage and integrate these diverse requirements effectively.
Is it necessary for a company to report on every topic and metric specified in the SASB Standard for its industry?
No, it is not necessary for a company to report on every topic and metric in the SASB Standard. The SASB Standards focus on financially material ESG issues, so companies should prioritise reporting on the aspects most relevant to their business and industry. This targeted approach aligns with the company’s ESG goals and helps streamline their sustainability reporting.
How can SASB Standards be incorporated into a company report?
SASB Standards can be incorporated into a company’s integrated report by aligning the reporting content with the SASB Framework, which provides industry-specific guidelines. Utilising ESG management tools and sustainability reporting software can facilitate the integration of SASB Standards into the integrated report, ensuring that the ESG information is presented clearly and effectively.
Does the IFRS Foundation evaluate, provide feedback on, or verify disclosures before publication?
The IFRS Foundation does not typically evaluate, provide feedback on, or verify disclosures before publication. Instead, the SASB develops the standards for sustainability reporting. Companies seeking SASB Certification may undergo an evaluation process to ensure compliance with the standards, but this is separate from the IFRS Foundation’s role.
Enhance Your SASB Reporting with Convene ESG

When you need a proven SASB reporting tool, look no further than Convene ESG. This all-in-one ESG reporting software suite can help you digitise financial materiality data for further development into precise, error-free SASB disclosures. And all with no extra hassle and minimal resource outlay.
Convene ESG also incorporates leading reporting frameworks and standards, such as the GRI Standards, CDP, TCFD, and more. This gives users a comprehensive toolkit for reporting to the widest range of stakeholders possible.
Learn more about SASB reporting and its potential benefits for our company by scheduling a walkthrough for Convene ESG. Explore our platform today.
Mel holds a bachelor's degree in Diplomacy and International Relations from the Ateneo de Manila University in 2018, with a specialization in East and Southeast Asian Studies. Her ESG experience is in working as a corporate ratings analyst with ISS ESG for almost 4 years, serving as topic specialist for occupational health and safety topic and industry specialist for Construction. During her free time, she enjoys crocheting and watching youtube videos on a variety of topics, all while spending time with her adopted stray cat.