Selecting the most fitting reporting framework can be challenging, especially with several standards in the ESG landscape. Even after selecting the reporting framework, companies are still overwhelmed about how to report on their impacts.
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) framework, one of the universal reporting frameworks available for adoption, guides companies to measure their sustainability impact by providing relevant ESG metrics and topics. Here is everything you need to know about GRI, its history, development, and framework.
What is the Global Reporting Initiative: History, Development, and Standards
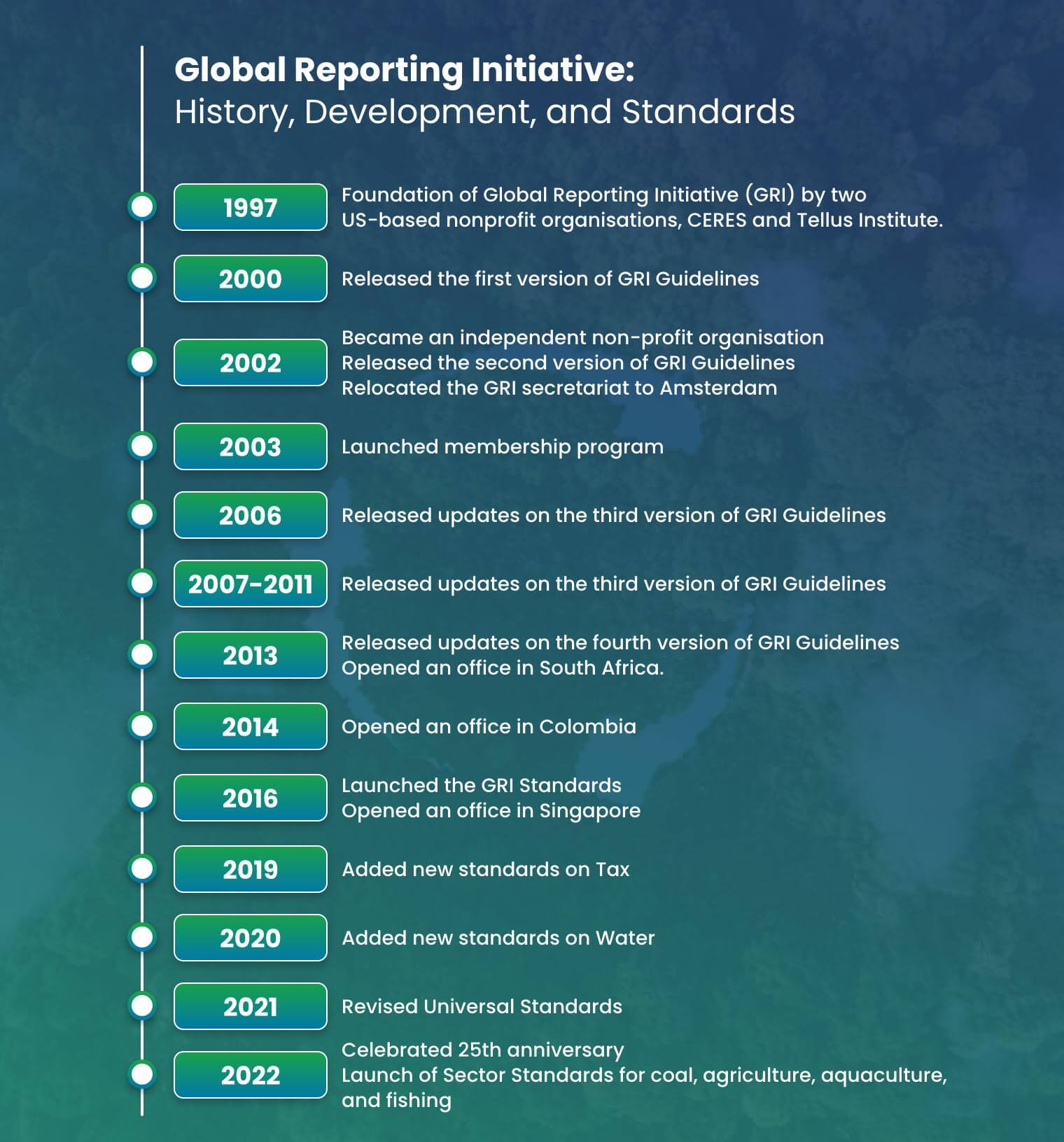
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is an international organisation founded in 1997 to promote global environmental sustainability reporting standards. It was initiated by Bob Massie of CERES and Allen White of Tellus Institute.
GRI was established to create a reporting framework that will help organisations measure and report on the impacts of business strategies on sustainable development and environmental conduct. It published its first sustainability guidelines in 2000, became a nonprofit in 2002, and started the establishment of global offices in 2007.
In 2016, GRI introduced global sustainability reporting standards and has since expanded its standards. In 2022, GRI marked its 25th anniversary by releasing sector standards for various industries.
What is GRI Framework and why is it important?
The GRI framework or GRI sustainability reporting standards is an easy-to-use reporting guideline for ESG analysis. With GRI’s standardisation and materiality principle, companies can gather and analyse data efficiently, allowing them to assess if their ESG goals are aligned with company policies and investor expectations.
GRI Standards are continuously improved and updated per module, removing the need for overhauling the whole reporting framework. This also allows companies to retain the efforts and budget allocated for previously established initiatives for sustainability. Below are a few reasons GRI is widely used across the globe:
- Uses a global reporting language — GRI’s primary goal is to enable a global reporting language for sustainability, which allows all concerned stakeholders to share a common understanding of your sustainability efforts.
- Enables easier benchmarking with peers — GRI’s data and structure can be easily compared with competing companies, providing transparency and accuracy to interested parties.
- Allows efficient KPI calculation — Adopting this framework allows companies to efficiently calculate their Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) or ESG metrics resulting in a deeper knowledge of impacts on the environment, economy, and society.
- Offers a wide range of topics — GRI’s 34 topic-specific standards allow listed companies worldwide to report both negative and positive impacts on certain topics, such as climate change, occupational health and safety, and data privacy.
- Mirrors intergovernmental expectations — GRI Standards embody the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Disclosures, which can be linked to reports on specific SDGs and their targets. The GRI also partnered up with organisations such as ISO, OECD, UN Global Compact, and UNEP to ensure that the standards are on par with global development initiatives.
- Promotes stakeholder inclusivity — One of GRI’s principles is stakeholder inclusiveness, requiring companies to identify their stakeholders. This, in turn, allows them to better address stakeholder expectations and interests.
Who uses the GRI Standards?

According to the Survey of Sustainability Reporting by KPMG in 2022, 78% of the world’s largest 250 companies by revenue now use the GRI reporting framework, an increase from 73% in 2020. Anyone who wishes to know more about the sustainable impacts of an organisation can access public reports typically on websites. The GRI framework is made up of multiple stand-alone standards (Universal, Sector, and Topic). This makes it flexible and adaptable to suit different groups and industries, mostly for-profit companies, nonprofit organisations, and governments.
Internationally recognised companies Unilever and Nike are actively reporting their impacts using GRI Standards. Unilever started applying the GRI Standards in 2002, while Nike began in 2005.
How are GRI reports used?
GRI Standards-compliant disclosures enable organisations and their stakeholders to fortify existing programs and policies and develop new ones based on actual ESG findings. With GRI reports, leaders can easily isolate unexplored market opportunities through a comparison of impacts with other organisations.
Investors can resort to GRI reports if they need to understand how certain organisations combine business and sustainable strategies to achieve their mission and goals. GRI reports offer value to stakeholders, such as investors, legislators, and scholars by giving them actionable intelligence.
What does the GRI framework cover?
GRI promotes transparency and accountability for businesses and organizations to publicly report on their impacts on economic, environmental, social, and human rights issues. The GRI framework for sustainability reporting covers three series of interconnected Standards in a modular system.
Universal Standards
Universal standards apply to all businesses and organizations and serve as a guide in identifying material topics. These standards have been revised to focus on delivering quality disclosures and responsible business conduct. The Foundation (GRI 101), General Disclosures (GRI 102), and Management Approach (GRI 103) cover the foundations of GRI reporting. Its key concepts include impact, material topic, due diligence, and stakeholder.
Sector Standards
Formed to improve reporting quality and consistency, these standards cover specific material topics, such as basic materials and needs, and group them into priority groups. You may use the sector standard that applies to your organization to identify material topics.
You can choose from the Oil and Gas sector (GR 11), Coal Sector (GR 12), and Agriculture Aquaculture and Fishing Sectors (GR 13). While Sector Standards uphold strict guidelines, they do not intend to replace your company’s internal process for identifying material topics.
Topic Standards
This set of standards covers specific topics, such as waste management and indirect economic impacts. It is divided into three subcategories—the Economic (GRI 200), Environmental (GRI 300), and Social (GRI 400) dimensions. You can choose from these topics to report specific information on your material topics.
Your company can opt to prepare your report based on the whole GRI Reporting Standards, a selected few Standards, or part of its contents. The latter allows you to report on specific purposes, such as Biodiversity and its impacts on relevant areas of ESG. Once decided, you can proceed with preparing the report.
What are the advantages of GRI reporting standards?
GRI Standards have grown in adoption over the last decade as organisations become aware of their benefits. Adhering to its reporting guidelines enhances your overall brand, reputation, and strategy.
Enhanced credibility and transparency with stakeholders
Stakeholder engagement is a mandated component in the process of producing a GRI-compliant sustainability report. Stakeholder Inclusiveness highlights the importance of stakeholder engagement in the GRI framework. This part of the reporting guide instructs the collection of the reasonable expectations and interests of stakeholders. It is meant to help in developing sustainable programs, making it to stakeholder demands.
GRI reports call for the disclosure of economic, environmental, social, and even government practices that are presented in globally standardised reports for the convenience of stakeholders. The publishing of impacts strongly exemplifies the transparency and accountability of an organisation, which also helps in increasing its credibility.
Informed decision-making and defined ESG risk mitigation
Creating an accurate GRI report involves intensive documentation of ESG indicators. The systematic collection of data required by the GRI framework makes internal assessments, benchmarking with peers and decision-making more straightforward. The standardised presentation of collected data makes performance evaluation and market forecasting more actionable, influencing decision-makers to develop more well-studied decisions.
Increased access to capital and markets
Organisations that report on their sustainability impacts, particularly those that have outstanding long-term performance, can increase their market value and appeal to creditors and investors faster than those that do not. An investor survey by McKinsey & Company in 2022, revealed that 85% of CEOs in their surveyed population said that they study ESG performance of prospects before making investment decisions.
Investors take the disclosure of ESG performance as a strong indicator of an organisation’s commitment to incorporating ethical initiatives into its business strategies in achieving sustainable financial growth.
What are the limitations of using GRI reporting standards?
Selective reporting of organisations
Sustainability reporting is a valuable process in communicating the economic, environmental, and social impacts to stakeholders. However, some organisations practice selective reporting and remove certain parts across required disclosures to protect their image and reputation. This can be usually done by controlling negative impacts and not properly engaging stakeholders. For instance, a business may choose to highlight only positive impacts and disregard the negative ones.
Resource-intensive
Creating reports according to the GRI Standards is complex. It demands time, resources and expertise. Because of these requirements, smaller organisations are more prone to challenges associated with their limited-scale operations. The GRI is often applicable to larger organisations. Smaller groups are likely to have more difficulty producing reports because they lack the requisite resources and reporting infrastructure.
Absence of an official auditing process
GRI does not officially certify GRI reports. They do not have a designated auditing body that focuses on the verification of disclosures, undermining its reliability. A systematic ESG assurance process carried out by an independent entity could be the most probable solution to this issue to protect the integrity and accuracy of GRI reports.
How to Integrate GRI Standards in ESG Reports

Organisations are encouraged to follow the GRI reporting framework process whilst considering the Standards set out above. A group of experts should be involved in each step to gather and analyse the organisation’s impacts and eventually produce a reliable sustainability report. After studying the system and elements of the GRI framework, especially the Universal Standards, organisations can proceed with these steps:
Step 1: Assessing your Impacts
Identify which day-to-day processes have impacts and then assess how they affect ESG factors. Refer to the Sector Standards to narrow down the topics and impacts that are most relevant to their organisation.
Having a dedicated report team will make it easier to determine and analyse the appropriate material topics for organisations. Here’s a step-by-step process for determining material topics.
- Step 1.1 — Understand the organization’s context
- Step 1.2 — Identify actual and potential impacts
- Step 1.3 — Assess the significance of the impact
- Step 1.4 — Prioritize the most significant impacts for reporting
Afterward, you can hold a kick-off meeting to discuss the plans.
Step 2: Discussing with Stakeholders
Engage with relevant stakeholders and experts to further narrow down which impacts to monitor. In this step, the primary goal is to determine the material topics that matter the most.
Step 3: Developing and Revising Content
Gather data on the material topics identified, and develop or revise content as needed. The Topic Standards will help identify which information to collect and report on. Next, set a meeting with internal executives to strengthen the action plan.
Step 4: Tracking your Progress
Organisations should track and ensure that their activities and processes are within the GRI framework. As this step can be prone to human error, organisations can implement digital ESG reporting software to effectively analyse their ESG performance and benchmark against their peers.
Step 5: Reporting on your Sustainability Strategy
Organisations can navigate their reports and include a GRI content index to make their data traceable. They can report on certain disclosures in the three series of standards. Reports can be in digital or hard-copy format and available in multiple locations.
Once organisations have completed these steps, they can notify the GRI and communicate with the public.
Future Developments on the GRI Framework
GRI has constantly refined its standards and reporting guidelines since it began. With more organisations committed to sustainability and transparency, the GRI framework is expected to play a key role in the future of sustainability reporting.
The GRI framework is capable of integrating with other well-known ESG reporting frameworks, such as SASB and TCFD, and more integrations are coming in the next years. GRI will continue to evolve in the following ways:
Heightened focus on financial and impact reporting
Sustainability reporting should be on equal footing with financial reporting. In a 2022 interview, the CEO of GRI, Eelco van der Enden revealed that they are working with international and intergovernmental organisations to put financial reporting into GRI reports. These organisations are the IFRS Foundation and the European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG).
Rapid digitalisation
Technological advancements are not entirely new in ESG reporting. Some groups have started adopting digital ESG reporting dashboards and AI. However, many organisations still resort to manual data collection and entry. This old-fashioned process is more susceptible to errors and can impede report production. Organisations committed to improving their ESG reporting are expected to implement more robust digital ESG solutions to meet the growing demand for impact reporting from stakeholders and investors.
Adopting GRI Framework in Sustainability Reports with Convene ESG
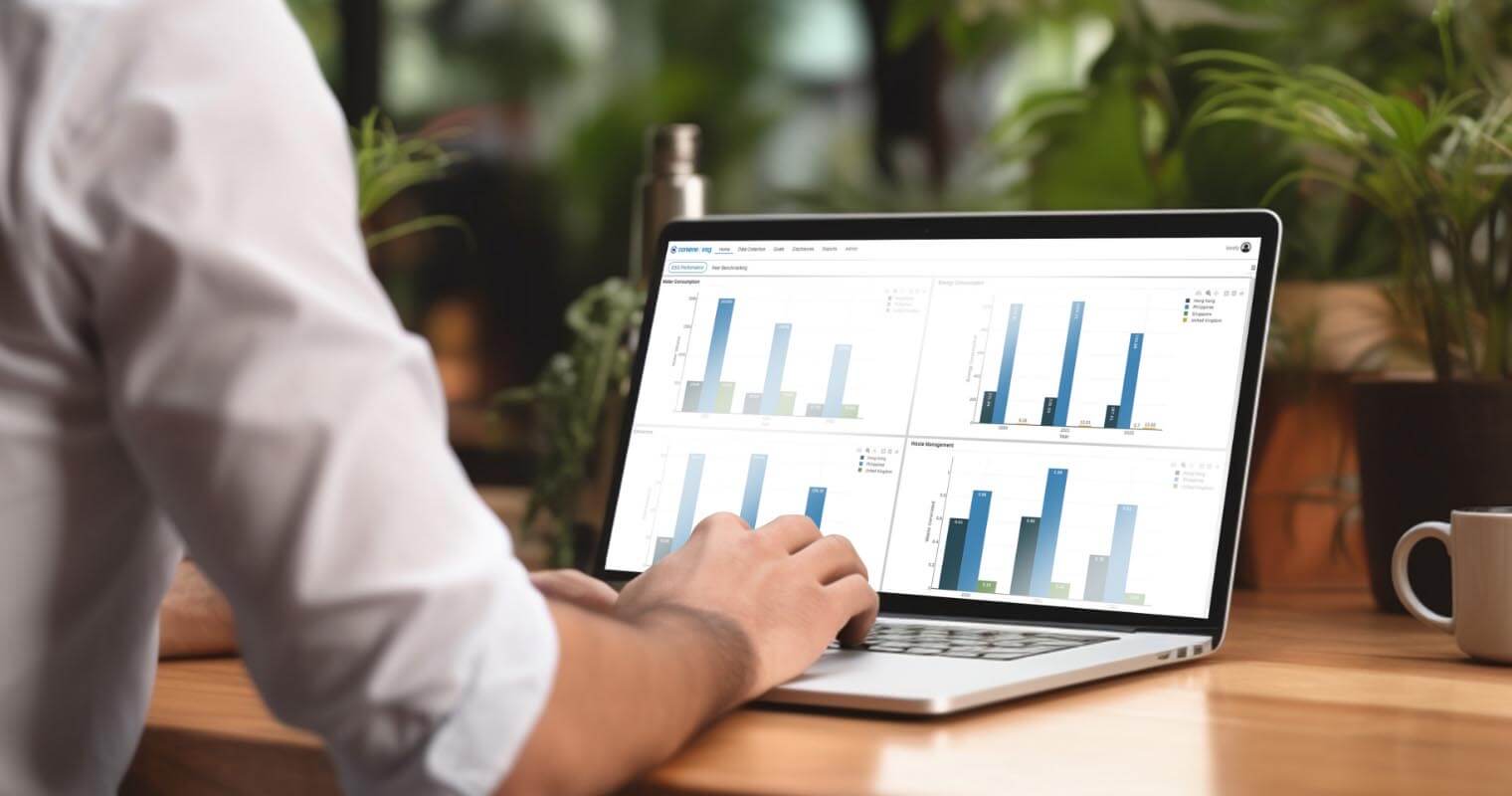

Adopting the GRI framework can improve stakeholder relations and create long-term sustainability for your company. To ensure a quality report, implement centralised ESG reporting software and be in control of your GRI reporting process without the complexity. Convene ESG takes an end-to-end approach to ESG and allows you to report not just on the GRI framework, but on other reporting standards as well.
Convene ESG offers a single source of truth and automates the long process of data gathering and analysis. It enhances visibility among stakeholders through its intuitive reporting features and interface. Convene ESG streamlines the end-to-end of ESG reporting with performance charts, progress dashboards, and automated compliance reports.
Learn more about how Convene ESG can help you create sustainability reports based on the GRI Standards.
Edward Quimba is a graduate of Consular and Diplomatic Affairs. He is currently taking MA International Studies major in Asian Studies at DLSU. He previously worked in the Environmental and Social Disclosure QualityScore (ESG Data Operations) team of ISS-ESG, and during his stint there, he was involved in ESG training for new hires, Data quality assurance, and ESG manual and platform development. He had his internship with Australian-New Zealand Chamber of Commerce, Makati where he helped in logistical tasks and organizing business events.














