Engaging suppliers is the linchpin of any credible net zero strategy. By actively involving suppliers in measuring, reducing, and managing emissions, businesses can gain more visibility and a clearer picture of their carbon footprint. All these lead to long-term sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals.
One of the biggest challenges in this effort is scope 3 emissions, the indirect emissions generated in the supply chain. These can make up as much as 90% of a company’s carbon footprint, and yet they are notoriously one of the hardest to control and measure accurately. While they’re difficult to pin down, most of their impact is linked to supplier activities. This is why supplier engagement matters. Understanding their role and what tools to support that collaboration adds to the visibility and shared accountability needed to move decarbonisation and ESG goals forward.
What are scope 3 emissions?
These emissions are indirect emissions generated by activities outside a company’s direct operations. They span everything from raw material extraction and manufacturing processes to transportation and product disposal, all things beyond regular day-to-day accounting and visibility. Coined as a “black box” for being an opaque scope and lacking transparency and visible processes, tracking these emissions has long been a challenge.
Challenges of Scope 3 Emissions
These are some of the main challenges companies face in managing scope 3 emissions:
- Lack of visibility in the supply chain: Many companies have no access to detailed and accurate oversight and information from their suppliers and consumers.
- Use of approximations: Without real and reliable data, businesses often rely on rough estimates based on financial data or industry averages, leading to inaccurate carbon inventories.
- Difficulty in pinpointing high-emission areas: With limited data, it’s tough to identify which parts of the supply chain or processes contribute most to emissions. Without knowing this, companies cannot effectively target their reduction efforts where they can make the most impact.
- Inconsistent standards for emissions reporting: Different organisations may follow different guidelines or methodologies for measuring emissions, leading to inconsistent and unreliable data.
- Supplier data limitations: Suppliers may not collect or share emissions data, creating a gap in necessary information.
Why Supplier Engagement is Key to Tackling Scope 3 Emissions
Given all these challenges, supplier engagement becomes crucial in addressing them. By this process of actively collaborating with suppliers to collect and refine sustainability data, companies can better track and manage their ESG practices. As scope 3 emissions represent the majority of carbon emissions, net zero is only achievable through an intentional, human-centric, and collaborative supplier engagement strategy.
Staying compliant with standards
Supplier engagement supports companies in staying up-to-date with sustainability standards and meeting climate-related reporting requirements. By conducting supplier ESG assessments, companies also get to evaluate a supplier’s overall ESG practices.
Aligning with climate frameworks and ensuring accuracy
Collaborating with suppliers helps companies align with climate frameworks like the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), ensuring regulatory compliance. Partnering with suppliers gets companies to collect accurate, real-time emissions data related to specific products, processes, and locations.
Targeting carbon reductions
Supplier engagement helps identify high-impact areas for carbon reduction, such as those under energy use, logistics and transportation, and sourcing of raw materials. This allows businesses to focus on the most effective solutions.
The Role of Supplier Engagement in Emission Reductions

Once businesses gather accurate emissions data, the next step is turning that information into concrete actions. The real progress in decarbonisation happens when data becomes a constant implementation of valuable actions. Smart approaches combine collaborative problem-solving with aligned incentives and supplier development.
Key strategies to integrate supplier engagement and turn data into real-world emissions reduction include:
Shared Innovation
Many companies and their suppliers co-develop, including renewable sourcing, energy efficiency, green materials, and circular design, to improve the value chain.
For example, the textile industry is a major contributor to global carbon emissions, responsible for up to 10% of total GHG emissions. Transitioning to a circular system, particularly through fiber-to-fiber recycling, could sustainably reduce emissions and reliance on raw materials. This transition requires overcoming barriers related to infrastructure, collaboration, and the adoption of innovative technology.
Incentive Alignment
Some companies incentivise low-carbon practices within their supply chains by prioritising suppliers that meet sustainability standards. Some companies also offer sustainability-linked initiatives, like Microsoft’s energy requirements and Walmart’s Project Gigaton, that support the sustainability efforts of its suppliers. These financial incentives align business goals with sustainability targets, encouraging suppliers to reduce emissions and contribute to the broader ESG goals.
Capacity Building for Suppliers
Providing support to suppliers is crucial in guaranteeing they can adopt and maintain best practices. This can be achieved through supplier forums, technical training, and workshops. Examples include initiatives like Danone’s Partner for Growth program and Unilever’s Supplier Climate Program that equips suppliers with tools, training, and clear guidance to help measure and reduce their carbon footprint. These efforts help businesses address scope 3 emissions by partnering with suppliers and developing targeted strategies for collaboration, reporting, and advancing sustainability.
Carbon Reduction Collaboration
Companies and their suppliers can co-develop solutions, such as energy-efficient technologies, process redesigns, and waste reduction strategies. Many large companies, like Google and Microsoft, have successfully partnered with their suppliers to set ambitious net zero targets, proving that supplier collaboration is a powerful way to reduce emissions.
Measuring Emissions Through Supplier Data
Supplier engagement allows companies to gain access to primary data, like tracing granular inventory and process-specific emissions details, that wouldn’t otherwise be available.
Supplier audits reveal critical data on carbon emissions from operations and the supply chain, along with energy use, waste management, and water sustainability practices. This provides a deeper level of verification, making the data reliable. It also provides a clearer picture of a company’s carbon footprint for accurate emissions reporting and targeted reduction strategies.
Supplier engagement delivers impact well beyond climate metrics:
- Cost reduction and efficiency gains: Detailed emissions data reveals inefficiencies, such as energy waste or excess transportation. Retailers, for instance, can cut up to 15-50% of scope 3 emissions using advanced tools and design for sustainability practices.
- Resilience and risk mitigation: By spotting high-carbon or unstable suppliers early, companies reduce the risk of climate-related disruptions and supply breakdowns.
- Investor and regulatory alignment: Global regulations such as the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) require value-chain emissions disclosure. Proactively ensuring compliance through supplier ESG assessments and alignment also opens doors to ESG-focused funding.
- Reputation and competitive edge: Consumers value sustainable credentials and are willing to pay more for them. Transparency in supply chains builds brand loyalty and strengthens investor relations.
The Five-Step Supplier Engagement Framework
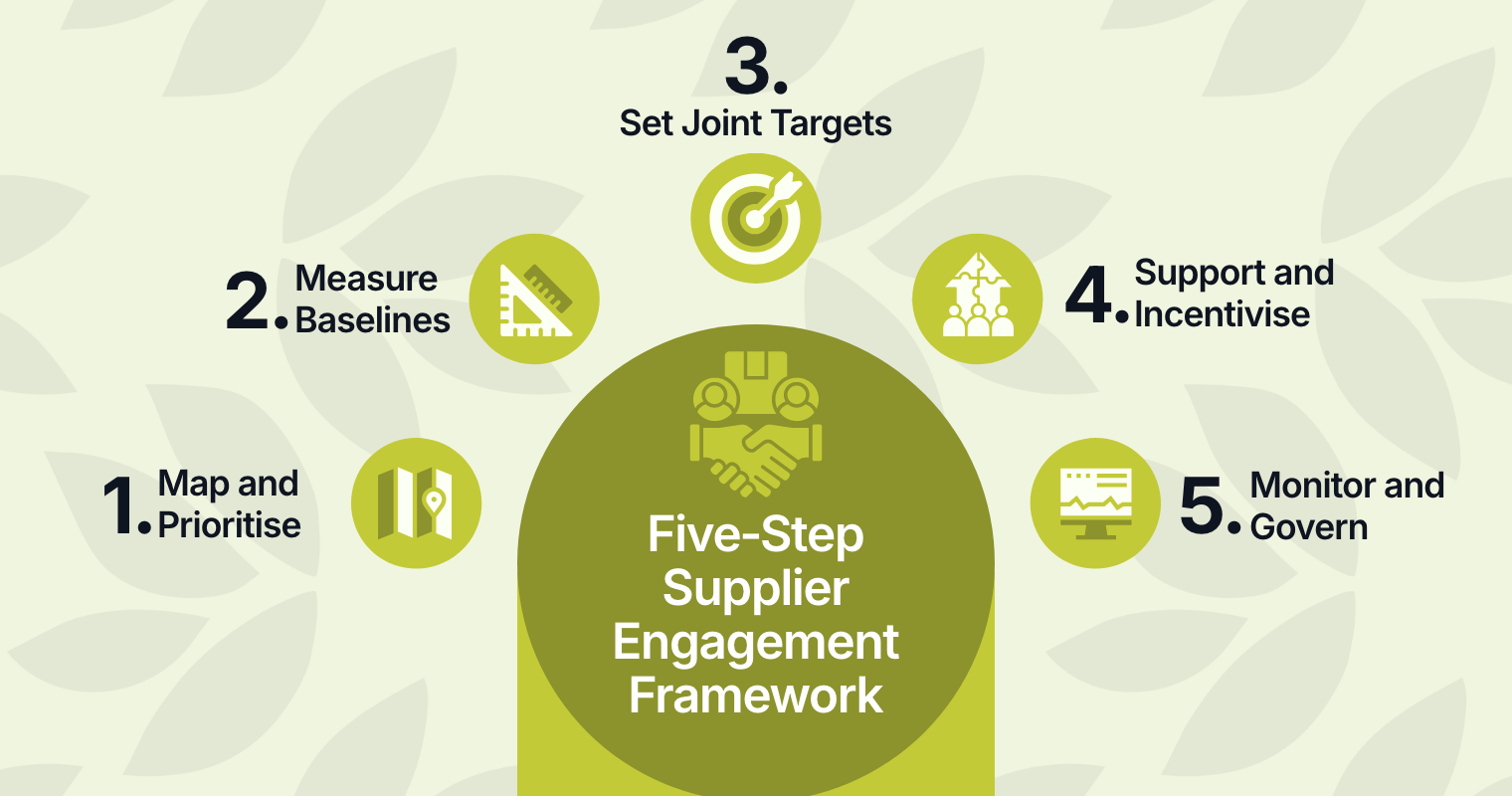
To successfully implement a supplier engagement strategy, businesses need a clear framework. Drawing from best practices used by leading companies, such as Deloitte’s model, the following steps are a structured approach for decarbonising supply chains through stronger supplier management.
- Map and prioritise: Start by identifying suppliers with the highest emissions. This allows businesses to target efforts where they’ll have the most impact.
- Measure baselines: Gather baseline emissions data, using both supplier-specific details and industry-standard emission factors.
- Set joint targets: Align with suppliers on carbon reduction goals, and include these targets in contracts to hold suppliers accountable.
- Support and incentivise: Provide suppliers with tools, training, and financial incentives to help them meet emissions reduction targets.
- Monitor and govern: Regularly monitor progress and integrate supplier engagement into broader procurements and sustainability goals.
Supplier Engagement: Success Stories in Action
Cutting emissions across supply chains isn’t easy, but some companies are showing what real progress can look like. From retail giants to food and tech leaders, these businesses are pushing forward with bold supplier programs that reduce emissions at scale. Here’s a glimpse into what’s working and what’s possible when companies take supplier engagement seriously.
Walmart: Collaboration
Context & Challenge
Walmart has acknowledged that the majority of its emissions lie within its value chain, not its operations. They are challenged with reducing emissions across their vast and complex supplier base. Given the slow renewable energy uptake, there is also a need for scalable low-carbon solutions.
Strategy & Action
Walmart launched Project Gigaton and invited suppliers to reduce emissions in key areas like energy, packaging, transportation, waste, product design, and nature. To keep suppliers involved, the company introduced a sustainable supply chain finance program in 2021. The initiative provides early payments to suppliers that meet science-based targets. This practical incentive helps increase participation and boost engagement even further.
Results & Impact
As of the latest update, over 3,500 suppliers, which represent over 70% of U.S. product sales, have joined Project Gigaton. They have avoided or reduced 750 million metric tonnes of emissions, which is 75% of Walmart’s 2030 goal of reducing 1 billion metric tonnes.
PepsiCo: Value Chain Transformation
Context & Challenge
Over 90% of PepsiCo’s total GHG emissions come from scope 3 sources. This includes agriculture, packaging, transport, and manufacturing. Managing such a broad and dispersed supply chain made data collection and emissions tracking even more complicated.
Strategy & Action
PepsiCo is taking bold steps to cut its emissions, committing to a 40% reduction in scope 3 emissions by 2030. This is supported by large-scale initiatives like regenerative agriculture, covering 7 million acres, and focusing on circular economy solutions for packaging. The company is working closely with over 200 suppliers through the Supplier Leadership on Climate Transition collaborative to help them decarbonise.
Results & Impact
PepsiCo continues to scale its supplier engagement strategies to meet its scope 3 targets and focuses on accelerating supply chain decarbonisation through partnerships, data-driven programs, and nature-based solutions.
Microsoft: Supplier Net Zero via Procurement
Context & Challenge
More than 96% of Microsoft’s total emissions are from scope 3, primarily from its supply chain. These emissions surged by 31% as the company expanded data center infrastructure to support AI growth, creating a tougher path toward overall decarbonisation.
Strategy & Action
As part of its carbon-negative 2030 goal, Microsoft will require its high-volume suppliers to shift to 100% carbon-free electricity by 2030, starting with its largest suppliers in 2025. To help implement this, Microsoft is working with a climate solutions partner that provides suppliers access to a platform for sourcing renewable energy more easily.
Results & Impact
While scope 1 and 2 emissions are on track, Microsoft’s approach to scope 3 now centers on supply-focused transformation. The supplier platform is designed to make the transition to carbon-free power more feasible at scale and better align supply chain emissions with the company’s goals.
Bridging Supplier Engagement with ESG Reporting Software
Reducing scope 3 emissions depends on precise supply chain insight, a coordinated supplier strategy, and aligned commercial frameworks. These are areas where ESG software solutions excel. They automate data collection, analytics, monitoring, and reporting, making supplier engagement scalable and measurable.
Convene ESG is equipped with built-in tools and features to simplify emissions, supplier audits, and compliance-ready reporting to global standards. With its dedicated supplier module, companies and sustainability teams can:
- Streamline data collection from multi-tier suppliers
- Monitor supplier performance and progress toward targets in real time
- Share transparent dashboards with stakeholders, regulators, and investors
Convene ESG software transforms what used to be a time-consuming manual process into an efficient, governance-ready workflow. It simplifies the complex task of managing emissions and helps businesses focus on collaborative innovation rather than manual reporting. Convene ESG provides a clear path toward a sustainable, net zero future.
Book a demo today and accelerate supplier engagement for scope 3 emissions management.















